TAMUctf 2021 Writeup
Contents
URL: https://tamuctf.com/challenges
去年のTAMU CTF 2020 (Writeup) は Network Pentest のチャレンジがあったりしたんですが、今年はなかったですね。残念〜。
800 points取りました。順位は、94thだったみたいです。(CTF TIME情報)
以下が解いたチャレンジです。
[Reversing]: Acrylic (100 points)
Challenge
This is an easy challenge. There is a flag that can be printed out from somewhere in this binary. Only one problem: There’s a lot of fake flags as well.
Hint: Try using GDB
Attachment:
- acrylic (ELF 64bit)
Solution
問題文にあるように Fake flag が沢山あるため、stringsコマンドは使えません。
(いちおう正解フラグもstringsで出てくるので、ひたすらSubmitしたら、そのうち当たりますけど。。)
GDBを使う前に、Ghidraでコードを見てみます。
|
|
main()は文字列を表示して終了するだけの関数です。
get_flag()は関数名から予想するに、flagを取得するための関数です。
GDBを使ってやることは、
- main() で一旦break
- get_flag() にもbreakをかけて、get_flag() へjump
- returnする直前にbreakをかけて、戻り値を確認
となります。get_flag() 自体は flag を printf しないので、GDB内で値を確認する必要があります。
gef➤ b main
gef➤ b get_flag
gef➤ jump get_flag
gef➤ disas get_flag
gef➤ b *0x00005555555546ab
gef➤ c
$rax : 0x0000555555756620 → "gigem{counteradvise_orbitoides}"
Flag: gigem{counteradvise_orbitoides}
[Pwn]: Handshake (150 points)
Challenge
Attack this binary and get the flag!
openssl s_client -connect tamuctf.com:443 -servername handshake -quiet
Attachment:
- handshake (ELF 32bit)
Solution
まず、問題文に出てくる openssl コマンドについてですが、News (announcement) で以下が出ていました。
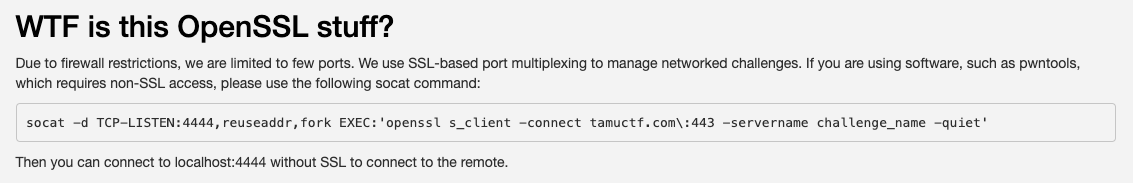
socatでトンネルを確立したら、あとはローカルでやってるのと同じ感覚でできるようです。
まずは、checksecを実行してみます。PIEは無効です。
$ checksec handshake
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)
vuln() 関数でBOFができます。他に、win()関数があるので、BOFを起こしてwin()に飛ぶだけです。
|
|
GDBでwin()のアドレスを確認。
gef➤ b main
Breakpoint 1 at 0x8049321
gef➤ r
:
gef➤ p win
$1 = {<text variable, no debug info>} 0x80491c2
書いたコード。
|
|
結果:
$ socat -d TCP-LISTEN:4444,reuseaddr,fork EXEC:'openssl s_client -connect tamuctf.com\:443 -servername handshake -quiet'
$ ./handshake_solve.py
[+] Opening connection to 127.0.0.1 on port 4444: Done
Correct! gigem{r37urn_c0n7r0l1337}
Flag: gigem{z1pT4st1c__$kiLl$$$}
Author CaptureAmerica @ CTF フラxxグゲット
LastMod 2021-05-04
